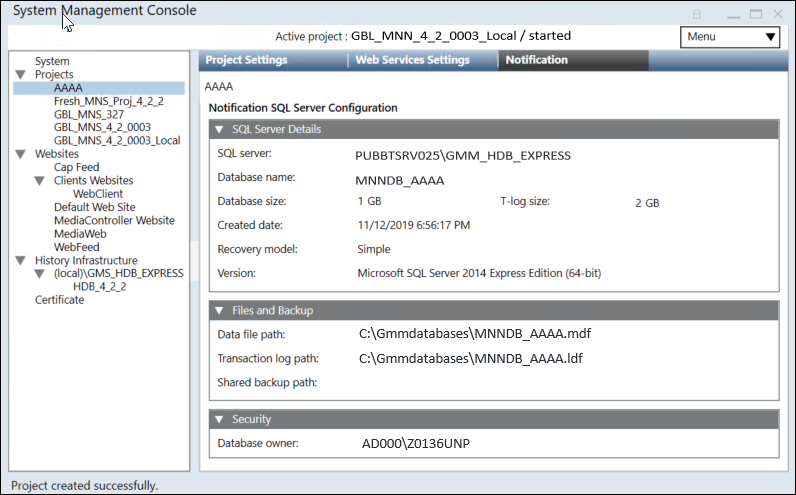
Notification Database Configuration in SMC
One step of notification project creation is to configure the Notification SQL Server.
SQL Server instance and SQL database are two different things. Notification needs separate SQL database to store its proprietary data.
You can do this using the Notification tab in SMC.
You can do this using the following expanders:
This section allows you to select a SQL Server to host the Notification database, fill in the log in details, and test the connectivity with the corresponding SQL Server.
- SQL Server: Select or manually enter the address of the SQL Server on which to create the new Notification database. Notification supports local as well as remote SQL servers.
- Database Name: Enter the name of the new Notification database. The database name must be unique on the targeted SQL Server.
- Test Connection: Test the connection to the targeted SQL Server before creating the new Notification database.
- Database Size: Select or manually enter the database size. The minimum database size that can be entered or selected is 1 GB and the maximum database size is 10 GB.
In case of huge data and high-performance expectations, you can prefer Standard and Enterprise edition, however it is not mandatory. - T-Log Size: Represents the transaction log size. The value of the T-Log size is dependent on the database size and is a multiple of two of the specified database size. For example, if the database size is 1 GB, then the T-Log size would be specified by the system as 2 GB.
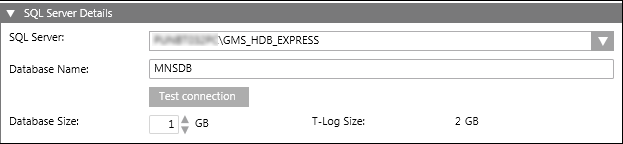
This section allows you to enter the file paths for the new Notification database as well as the folder path where SQL Server will place backup files created from the Notification database.
- Data File Path: Browse or manually enter in the data file path of the Notification database. The path has to be entered local to the SQL Server.
- Transaction Log Path: Browse or manually enter the transaction file path of the Notification database. The path has to be entered local to the SQL Server.
- Shared Backup Path: Browse or manually enter the shared backup path of the Notification database. Path must be entered local to the SQL Server.
This path is needed when the database is present on remote SQL server (different from Notification server). In this situation, you need to configure the Shared Backup Path in SMC. This path must be accessible by the Notification server and SQL server so that you can make the backup.

NOTE:
When using a remote SQL Server (SQL Server running on a machine other than the Notification installation):
a) All file and folder paths should be specified local to the SQL Server machine, or in other words, as the SQL Server machine sees them. When creating the Notification database on a remote SQL Server, do not use the Browse functionality because Browse only shows the file system of the machine where the System Management Console is executed. Instead, manually type in file and folder paths that are valid on the SQL Server machine.
b) For the Shared Backup Path, when using a remote SQL Server, specify a shared folder path in UNC format so that both the SQL Server machine as well as the main Notification installation can access the generated backup files. Example of a path in UNC format: \\FileServer\MNSBackup.
This section allows you to select the database owner.

- Database Owner: Select the owner of the Notification project database. When you click Browse, the Select User dialog box displays. Select the database owner from the Current Station or from the Other Domains. For more information, refer to the Select User Dialog Box section of Desigo CC.
Tips
- For security purposes, the Notification system stores the user credentials as well as device credentials in a file or database in an encrypted or hashed format.
- Notification uses a cryptographic hash algorithm to hash the user PIN in combination with a salt value. Additionally, Notification uses public key encryption (public key to encrypt, private key to decrypt) to protect device or service passwords when stored in a file or database.
- As part of the security feature, in the Password field, the number of dots or asterisks shown has no correlation with the actual length of the saved PIN. For example, the user interface displays 8 characters even if the configured PIN is only four characters in length.
Access Rights To… | Database Owner |
Create, restore, or upgrade database | X |
Edit database Owner or database user | X |
Read and write to the database | X |
